Hi friends,
I would like to start this one by thanking you for taking your precious time to read me every single week. It truly fuels me to keep going!
While writing the last article, I stumbled upon something called the Gartner Hype Cycle. It’s a very interesting way to assess the life cycle of technological innovations. Let’s break it down!
What’s the Gartner Hype Cycle?
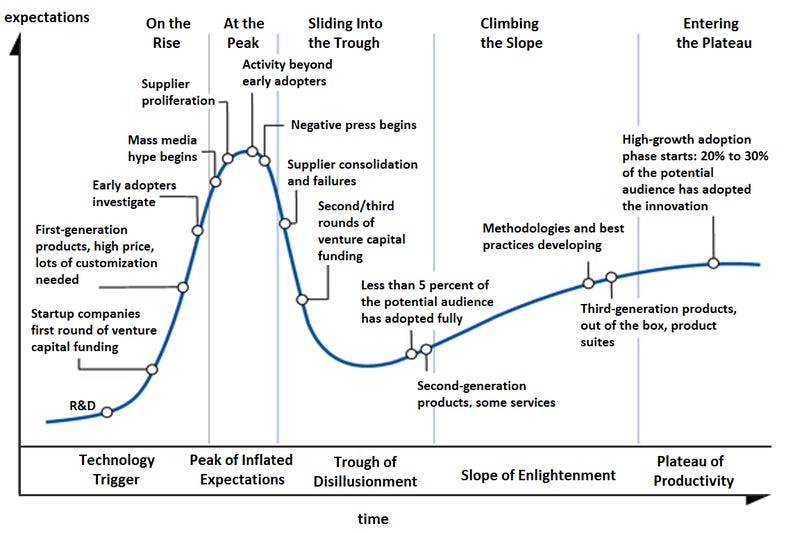
The Hype Cycle is a graph that represents the maturity, adoption, and social application of more than 2,000 unique technologies, bundled in clusters, which are expected to greatly impact business and society over the next 2-10 years. Published by Gartner annually, it gives a general view of how a technology or application will evolve over time and its relevance in solving real business problems.
The Hype Cycle splits the life cycle of emerging technologies through five phases of maturity:
Innovation Trigger: A technological breakthrough kicks things off, and then media interest trigger significant publicity. At this stage, only proofs-of-concept exist, commercial viability is unproven, and companies are scared to invest.
Peak of Inflated Expectations: The early publicity results in several success stories, accompanied by many failures. At this stage, some companies start taking action, but many do not.
Trough of Disillusionment: The interest in the technology diminishes as experiments and implementation fail to deliver. At this stage, investments continue only if the surviving providers improve their products enough to satisfy early adopters.
Slope of Enlightenment: 2nd and 3rd-generation products start to appear and enterprise use cases for the technology become widely understood. At this stage, many companies are funding pilots, except the old guards.
Plateau of Productivity: Mainstream adoption starts to take off and criteria for assessing the viability get clearly defined (i.e. the technology's market applicability and relevance are paying off). At this stage, the technology will continue to grow if the market is broad enough.
How Is It Useful?
Companies and investment firms use the Hype Cycle to get educated about the promise of emerging technology within the context of their industry before deciding if they should do an early move. Amongst other things, the Hype Cycle helps to: 1) separate hype from real drivers of a technology’s commercial applications, 2) reduce investment risks, and 3) estimate the time until mainstream adoption.
It’s important to remain careful while using this model because it’s much closer to subjectivity than science — few technologies actually travel through an identifiable hype cycle. Moreover, an analysis of Gartner Hype Cycles shows that most of the important technologies adopted since 2000 were not identified early in their adoption cycles.
Key Takeaways from the 2022 Gartner Hype Cycle
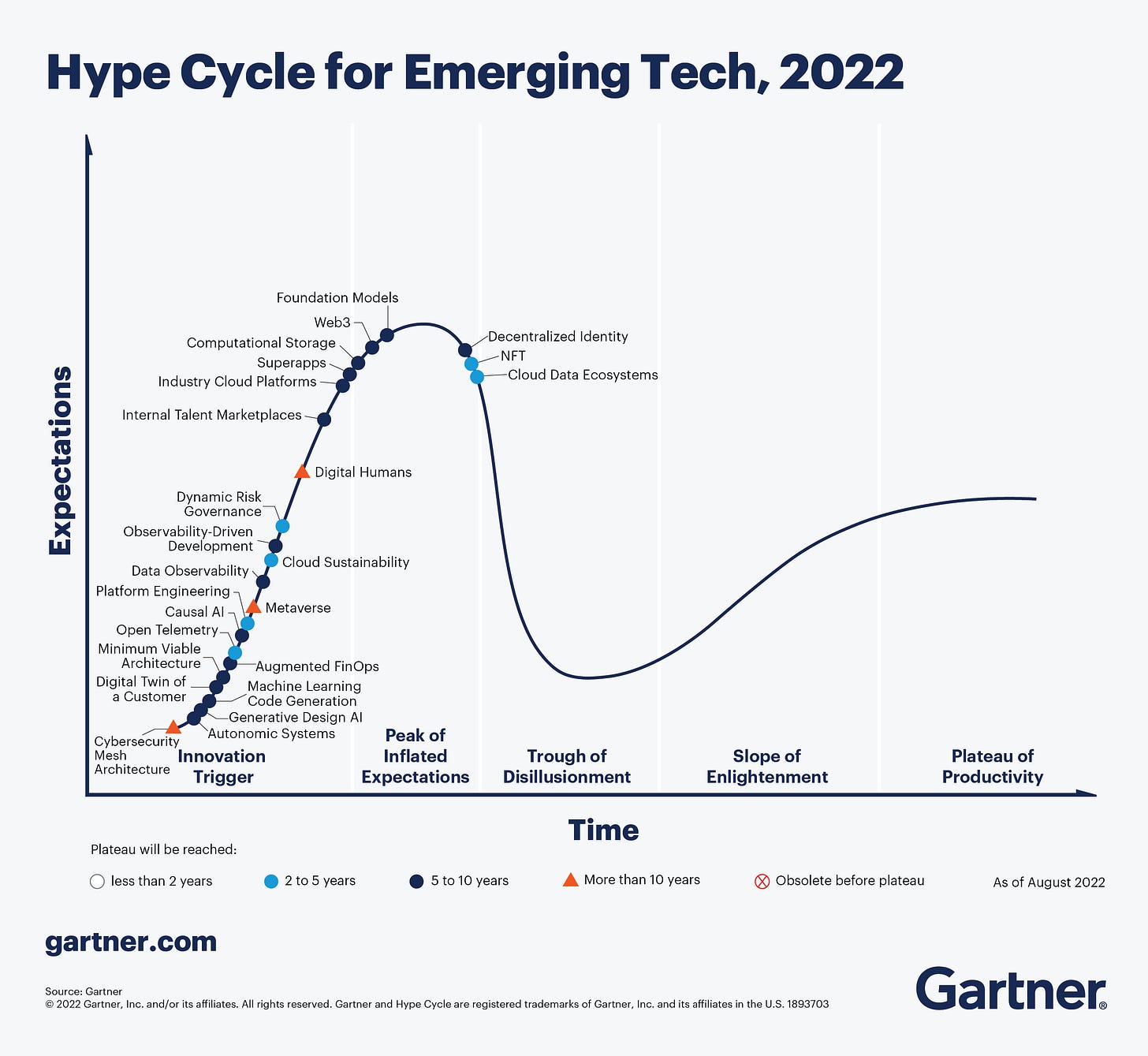
The 2022 Gartner Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies features 25 “must know” innovations with multiple use cases. All these technologies are at an early stage, and it’s highly uncertain how they will develop. However, we see a convergence around three general themes — immersive experiences, AI automation, and technology delivery.
Theme 1: Evolving/Expanding Immersive Experiences
These technologies provide individuals more control over their data and expand their range of experiences into virtual ecosystems. For enterprises, they provide new ways to reach customers and open up new revenue streams. Here’s my ranking of the most transformational innovations in this bucket:
Digital Twin of the Customer (DToC): Dynamic virtual representation of a customer that uses both online and physical interactions to accurately simulate the customer experience and provide context and predictions of future consumer behaviors. This should take 5-10 years until mainstream adoption.
Decentralized Identity (DCI): Allows users to take back control of their digital identities by leveraging technologies such as blockchain (or other DLTs), and digital wallets.
Non-fungible token (NFT): Unique programmable blockchain-based digital item that publicly proves ownership of tokenized digital and physical assets.
Internal Talent Marketplaces: Platforms that match internal employees and pools of contingent workers to time-boxed projects and various work opportunities, with no recruiter involvement.
Digital Humans: AI-driven digital avatars that have some of the characteristics, personality, knowledge, and mindset of a human.
Other critical technologies that will power immersive experiences include web3, metaverse, and super-app.
Theme 2: Accelerated AI Automation
These technologies aim at accelerating the creation, development, and deployment of specialized AI models to deliver more accurate predictions and faster decisions. Here’s my ranking of the most transformational innovations in this bucket:
Autonomic System: Self-managing physical or software systems that manage themselves automatically through adaptive technologies. These could help with business implementation when traditional AI techniques cannot. However, it will take 5-10 years until mainstream adoption.
Generative Design AI: The use of AI, ML, and natural language processing (NLP) technologies to generate and develop user flows, screen designs, content, and presentation-layer code for digital products.
Machine Learning Code Generation: Cloud-hosted ML models that plug into integrated development environments (IDEs) and provide suggested code based on natural language descriptions or partial code fragments.
Other critical technologies accelerating AI automation are causal AI, and foundation models.
Theme 3: Optimized Technologist Delivery
These technologies provide insight that will help business operations by optimizing and accelerating product & service delivery. Here’s my ranking of the most transformational innovations in this bucket:
Cloud Data Ecosystems: Cohesive data management environment that supports whole data workloads (i.e. from exploratory data science all the way through production data warehousing) and provides streamlined delivery and comprehensive functionality. It will take 2-5 years until mainstream adoption.
Augmented FinOps: Automates traditional DevOps concepts to financial governance, budgeting, and cost optimization through the application of AI and ML.
Computational Storage (CS): Offloads host processing from CPUs to storage devices.
Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture (CSMA): An emerging approach to security controls architecture that improves overall security effectiveness by eliminating siloes.
Dynamic Risk Governance (DRG): Customizes risk governance appropriately to each risk, enabling organizations to better manage risks and lower their assurance costs.
Other critical technologies that will optimize tech delivery are cloud sustainability, data observability, industry cloud platforms, minimum viable architecture, observability-driven development, platform engineering, and OpenTelemetry.
Hope you liked this one, even if you’re not tech-savvy!
Cheers,
Benjamin